Art Lovers discussion
Art History
>
Art Trivia of the Day (2011: April through June)
date newest »
newest »
 newest »
newest »
 Happy birthday to Fragonard on April 5, 1732 in Grasse.
Happy birthday to Fragonard on April 5, 1732 in Grasse.[image error]
Stolen Kiss
Jean-Honoré Fragonard was a French painter of the rococo age who became a favorite in the courts of Louis XV and Louis XVI for his delicately colored scenes of romance, often in garden settings. Fragonard began to study painting at the age of 18 in Paris with Jean Baptiste Simeon Chardin, but he formed his style principally on the work of his next master, Francois Boucher. Fragonard won the Prix de Rome in 1752.
After studying for three years with the French painter Carle Van Loo, he studied and painted for six years in Italy, where he was influenced by the paintings of the Venetian master Giovanni Battista Tiepolo. Fragonard first painted in a style suitable to his religious and historical subjects. After 1765, however, he worked in the rococo style then fashionable in France. These later paintings, the works for which he is best known, reflect the gaiety, frivolity, and voluptuousness of the period. They are characterized by fluid lines, frothy flowers amid loose foliage, and gracefully posed figures, usually of ladies and their lovers or peasant mothers with children.
The French Revolution (1789-1799), which destroyed the nobility on which Fragonard depended for commissions, ruined him financially. Although befriended by Jacques Louis David, the leading painter of the new French classical school. His chief work was decorative panels commissioned by Madame du Barry, mistress of Louis XV, for her chateau at Louveciennes. She rejected the panels as unsuitable. Fragonard did not adjust to the new style and died poor in Paris on August 22, 1806.
[image error]
[image error]
[image error]
 Happy birthday to Raphael on (Good Friday) April 6, 1483 in Urbino, Duchy or Urbino (Italy).
Happy birthday to Raphael on (Good Friday) April 6, 1483 in Urbino, Duchy or Urbino (Italy).
probably self portrait from his teens
Raphael, like Michelangelo and Leonardo da Vinci, is one of the most famous artists of Italy's High Renaissance and one of the greatest influences in the history of Western art. Immensely talented, he first studied with his father and then as an assistant to the great master Pietro Vannucci, known as Perugino. Raphael (also known as Raffaello Sanzio) worked in Florence (1504) and earned a reputation as a productive and much-admired painter before going to Rome sometime after 1508. In Rome he was commissioned by Pope Julius II to create the large-scale fresco The School of Athens, as well as other decorative work at the Vatican. Raphael also took over as architect of St. Peter's after the death of Donato Bramante (1514), contributed ten tapestries to the Sistine Chapel and painted some of the most prized and reproduced holy pictures of the era, including The Sistine Madonna and Transfiguration. His work is often cited for its harmony and balance of composition, and his early death on Good Friday (his 37th birthday) is considered by many experts to be one of the great tragedies of art history. (answers.com)
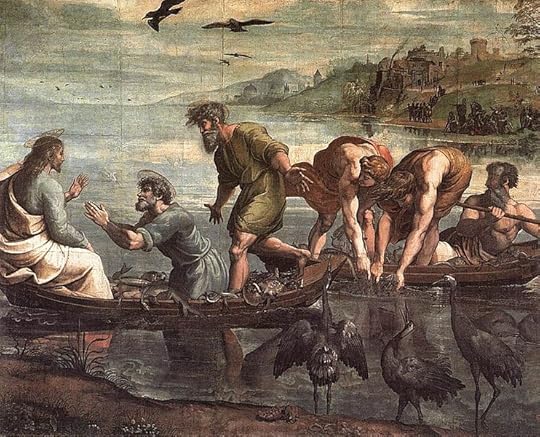

The Miraculous Draught of Fishes (1515)

The Stanza della segnatura ("Room of the Signatura") was the first to be decorated by Raphael's frescoes.
Raphael’s rooms: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stanza_d...

The small Cowper Madonna , c. 1505, Oil on wood, National Gallery of Art, Washington
 Happy birthday to Gustave Moreau on April 6, 1826 in Paris, France.
Happy birthday to Gustave Moreau on April 6, 1826 in Paris, France.[image error]
Self-portrait of Gustave Moreau, 1850
Moreau developed a distinctive style in the Symbolist mode, becoming known for his erotic paintings of mythological and religious subjects. Such works as Oedipus and the Sphinx (1864) and Dance of Salome (1876) have often been described as decadent. He made a number of technical experiments, including scraping his canvases; his nonfigurative paintings, done in a loose manner with thick impasto, have led some to call him a herald of Abstract Expressionism. He died on April 18, 1898. (answers.com)
[image error]
Oedipus and the Sphinx, 1864, oil on canvas, The Metropolitan Museum of Art
This painting represents the moment when Oedipus confronts the winged monster outside Thebes and must solve her riddle to save his life as well as those of the besieged Thebans. The work shows Moreau's awareness of Ingres's version of the subject (Musée du Louvre, Paris), painted in 1808, which Moreau had sketched. It also demonstrates his familiarity with works by the early Renaissance painter Andrea Mantegna, whose paintings Moreau had studied at the Louvre. Moreau's choice of a mythological subject and his deliberately archaizing style distinguished his painting from the realist and naturalist currents of the 1860s.
[image error]
Salomé Dancing Before the Head of St. John the Baptist, Graphite, watercolor and gouache on cream wove paper, The Metropolitan Museum of Art
[image error]
Galatea, Circa 1880, Oil on wood, Paris, Musée d'Orsay
 Carol wrote: "Happy birthday to Raphael on (Good Friday) April 6, 1483 in Urbino, Duchy or Urbino (Italy).
Carol wrote: "Happy birthday to Raphael on (Good Friday) April 6, 1483 in Urbino, Duchy or Urbino (Italy).probably self portrait from his teens...
His work is often cited for its harmony and balance of composition, and his early death on Good Friday (his 37th birthday) is considered by many experts to be one of the great tragedies of art history...."
I wonder what went on at that final birthday party. Damn shame. Nobody seems to know, I think it was hushed up. It may have been an undiagnosed condition like a heart murmur, but I suspect that it may have been binge drinking. Raphael was very well liked and, apparently fun to be with, and had a reputation as a party animal.
 Carol wrote: "Happy birthday to Gustave Moreau on April 6, 1826 in Paris, France.
Carol wrote: "Happy birthday to Gustave Moreau on April 6, 1826 in Paris, France.Self-portrait of Gustave Moreau, 1850
Moreau developed a distinctive style in the Symbolist mode, becoming known for his erotic..."
He was also one of the most outstanding art teachers who ever lived. On of the indications of this is how he brought out the individual character of each of his students, whose styles were nothing like his own.
Here's an interesting JSTOR article synopsis
 Ed wrote: "I wonder what went on at that final birthday party. Damn shame. Nobody seems to know, I think it was hushed up. It may have been an undiagnosed condition like a heart murmur, but I suspect that it may have been binge drinking. Raphael was very well liked and, apparently fun to be with, and had a reputation as a party animal. ..."
Ed wrote: "I wonder what went on at that final birthday party. Damn shame. Nobody seems to know, I think it was hushed up. It may have been an undiagnosed condition like a heart murmur, but I suspect that it may have been binge drinking. Raphael was very well liked and, apparently fun to be with, and had a reputation as a party animal. ..."He is said to have had many affairs, but a permanent fixture in his life in Rome was "La Fornarina", Margherita Luti. According to Vasari, Raphael's premature death was caused by a night of excessive sex with Luti, after which he fell into a fever (and, not telling his doctors that this was its cause,) was given the wrong cure, which killed him. (wiki)
[image error]
Portrait of a Young Woman (La fornarina), 1518-1519, Oil on wood, National Gallery of Ancient Art, Rome
 On April 7, 1978 a Gutenberg bible sold for a record $2.2 million in NYC. It was bought by Martin Breslauer for the state museum of Baden Wurttemberg.
On April 7, 1978 a Gutenberg bible sold for a record $2.2 million in NYC. It was bought by Martin Breslauer for the state museum of Baden Wurttemberg.
The Gutenberg Bible was the first book ever printed (in 1456) with moveable type. About 180 versions are believed to have been printed originally. Many of the remaining Bibles have been broken down into sections. Only 21 are believed to be completely intact. Today a fully-intact Gutenberg Bible is valued at $25-35 million.
The Morgan Library & Museum, of course, is the only institution worldwide to possess (not one but) three copies of the Gutenberg Bible. They have one copy on vellum and the other two copies on paper. For a digital facsimile: http://www.themorgan.org/collections/...
It is one of my favorite places to visit and the bibles are easy to see in their glass cases.
[image error]
 I'm not very interested in bibles. But I do love beautiful manuscripts and manuscript illumination. Lovely.
I'm not very interested in bibles. But I do love beautiful manuscripts and manuscript illumination. Lovely.
 Happy birthday on April 9th to . . .
Happy birthday on April 9th to . . . . . . photographer Eadweard Muybridge.

Born April 9, 1830, Kingston upon Thames, Surrey, England. He immigrated to the U.S. from England as a young man, and in 1868 his photos of Yosemite Valley made him famous. Hired by Leland Stanford to photograph a trotting horse in motion, to test Stanford's contention that it lifted all four legs simultaneously, he developed a special fast shutter for his battery of 12 to 24 cameras, and in 1877 he proved Stanford right. He lectured widely on animal locomotion, illustrating his lectures with his zoopraxiscope, a predecessor of the movie projector. His extensive photographic studies of human movement (1884 – 87) have been useful to artists and scientists. He died May 8, 1904, Kingston upon Thames. (answers.com)

The Domes from Merced River, Yosemite Valley, c. 1874 albumen print, George Eastman House

Galloping horse set to motion using photos by Eadweard Muybridge.

American bison cantering – set to motion using photos by Eadweard Muybridge
. . . . painter Charles Burchfield.

Born April 9, 1893, Ashtabula Harbor, Ohio. He attended the Cleveland School of Art and, after service in World War I, worked as a wallpaper designer in Buffalo, N.Y. In the 1920s and '30s he was one of the leading painters of American life; his work was associated with Edward Hopper's in its portrayal of the loneliness and bleakness of small-town life (e.g., November Evening, 1934). In the 1940s he abandoned realism for a more personal interpretation of nature, emphasizing its mystery, movement, and color from season to season (e.g., The Sphinx and the Milky Way, 1946). He died Jan. 10, 1967, Gardenville, N.Y. (answers.com)
[image error]
November Evening

"The Sphinx and the Milky Way," 1946. Opaque and transparent watercolor, chalk, and crayon on wove water color paper, 52 5/8 x 44 3/4 inches.

. . . painter Victor Vasarely.
[image error]
Born April 9, 1908, Pécs, Hungary. Trained in Budapest in the Bauhaus tradition, he moved to Paris in 1930 and supported himself as a commercial artist. In the 1930s he was influenced by Constructivism, but by the 1940s he was painting animated surfaces of geometric forms and interacting colors. His style reached maturity in the mid 1950s and 1960s, with the use of more vibrant colors to increase the sense of movement through optical illusion, as in Sirius II (1954), and he became one of the leading figures of the Op art movement. He died March 15, 1997, Paris, France. (answers.com)
[image error]
Marc Positive
[image error]
zebra
[image error]
Sirius II
 More Jeopardy trivia...
More Jeopardy trivia...Pulitzer Prize winner Robert Frost remarked that this is what gets "lost in translation".
Everyone is welcome to comment. If you would like to guess the answer just skip to where you can post your comment rather than reading the preceding comments if as to not influence your guess.
 Heather wrote: "More Jeopardy trivia...
Heather wrote: "More Jeopardy trivia...Pulitzer Prize winner Robert Frost remarked that this is what gets "lost in translation".
What happened to the quiz about the 4 paintings in the Met collection? I had no idea and made a wild guess!
I don't know what Frost said but I thought Bill Murray and Scarlett Johansson were fantastic in the movie!
 That's a good question, Monica. I have no idea which four paintings are the ones they are talking about so I wouldn't know the answer. But I posted the country that 1/3 of them came from is The Netherlands.
That's a good question, Monica. I have no idea which four paintings are the ones they are talking about so I wouldn't know the answer. But I posted the country that 1/3 of them came from is The Netherlands.Anyway, Frost said it's Poetry that gets lost in translation. I would have guessed love, but obviously that was wrong. Believe it or not, that is what 2 out of the 3 contestants guessed, too.
 Happy birthday to Robert Delaunay born April 12, 1885, Paris, France.
Happy birthday to Robert Delaunay born April 12, 1885, Paris, France. 
He spent his early career as a part-time designer of stage scenery and came under the influence of Neo-Impressionism, Fauvism, and Cubism. In 1909 – 11 his color experiments culminated in a series of paintings of the Eiffel Tower, which combined fragmented Cubist forms with dynamic movement and vibrant color. The introduction of bright color to Cubism — a style that came to be known as Orphism — distinguished his work from that of the more orthodox Cubist painters and influenced the artists of Der Blaue Reiter. With his wife, the Ukrainian-born painter and textile designer Sonia Terk Delaunay (1885 – 1979), he painted abstract mural decorations for the 1937 Paris Exposition. Delaunay died Oct. 25, 1941 in Montpellier.

wife Sonia

Red Eiffel Tower, 1911–12. Oil on canvas, Guggenheim Museum
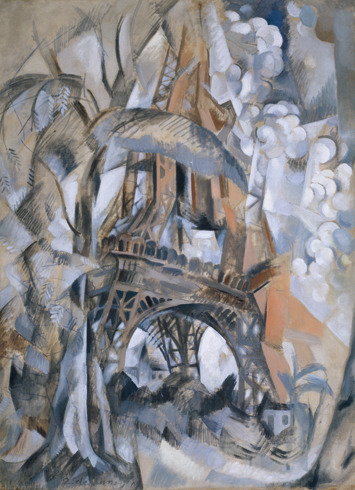
Eiffel Tower, 1911 (dated 1910 by the artist). Oil on canvas, Guggenheim Museum

Tour Eiffel et Champ de Mars

Saint-Séverin No. 3, 1909–10, Oil on canvas, 45 x 34 7/8 inches, Guggenheim
Delaunay explored the developments of Cubist fragmentation more explicitly in his series of paintings of the Eiffel Tower. In these canvases, characteristic of his self-designated “destructive” phase, the artist presented the tower and surrounding buildings from various perspectives. Delaunay chose a subject that allowed him to indulge his preference for a sense of vast space, atmosphere, and light, while evoking a sign of modernity and progress. Like the soaring vaults of Gothic cathedrals, the Eiffel Tower is a uniquely French symbol of invention and aspiration.

Simultaneous Windows (2nd Motif, 1st Part) (Les fenêtres simultanées [2e motif, 1re partie]), 1912. Oil on canvas, 21 5/8 x 18 1/4 inches (55.2 x 46.3 cm). Guggenheim Museum

Circular Forms, 1930, Oil on canvas, 50 3/4 x 76 3/4 inches, Guggenheim Museum
 Sorry I haven't posted in awhile but I didn't want to repeat the same people
Sorry I haven't posted in awhile but I didn't want to repeat the same peoplethat I posted last year.
Happy birthday to Bertram Grosvenor Goodhue born on April 28, 1869 in Pomfret, CT.
[image error]
Bertram Grosvenor Goodhue was an innovator in architecture by combining Gothic and Hispanic designs with modern ideas. He revolutionized church architecture by reawakening medieval traditions, and his fanciful Spanish Churrigueresque buildings for the Panama-California Exposition brought new energy to Spanish Colonial Revival architecture in the United States. He is also known for designing two typefaces (Cheltenham and Merrymount). Goodhue is considered an American modernist.
Goodhue never attended college. Instead, at age fifteen he went to work in the New York office of Renwick, Aspinwall and Russell. In 1898, he formed his own partnership with Cram, Goodhue and Ferguson. Although Goodhue's early works were noted for their high Gothic style, he later adopted a lighter, Romanesque style. By the end of his career, his work tended toward simple, classical lines. Goodhue died on April 23, 1924 in NYC.
[image error]
In 1915, the gates to the Panama Canal swung open. To celebrate, San Diego - the first North American port of call on the Pacific Coast - launched a spectacular exposition. The chief designer for the event was Bertram Grosvenor Goodhue, who had a fascination for Gothic and Hispanic styles. Goodhue did not want the cold, formal Renaissance and Neoclassical architecture that was normally used for expositions and fairs. Instead, he envisioned a fairytale city with a festive, Mediterranean flavor.

Casa del Prado in Balboa Park is a lavish re-invention of Spanish Baroque, or Churrigueresque, architecture.

For a railroad heir, Goodhue designed a colonnaded villa in Montecito, CA, with Persian-inspired azure pools.
TYPEFACES --
MERRYMOUNT

[image error]
Cheltenham typeface was designed in 1896 by American Architect Bertram Grosvenor Goodhue for the Cheltenham Press in New York. The typeface is influenced by the Arts and Crafts movement popular at the time, and was designed with best possible legibility in mind, incorporating long ascenders and short descenders. It has proved a popular and widely-used typeface in the United States. Even as recently as 2003, the New York Times took the decision to use Cheltenham as a single font family replacement for six other headline typefaces used previously.
BOOK ART --
Just for fun! In the "old days" (before computers) when things were actually drawn by hand, Goodhue designed the border for this alphabet book.)

“Q Is for the Queen”
Oliver Herford. An Alphabet of Celebrities. Boston: Small, Maynard & Company, 1900.
Illustrated by: Oliver Herford (1863 – 1935). Border decorations by: Bertram Grosvenor Goodhue (1867 – 1924-- chiefly known as an architect); Cover Design by: E.B. Bird [Elisha Brown Bird, 1867 – 1943.
 Gauguin was born on June 7, 1848 in Paris. He is probably best known for his young primitive Polynesian girls in bold colors. Here are a few of his works which differ.
Gauguin was born on June 7, 1848 in Paris. He is probably best known for his young primitive Polynesian girls in bold colors. Here are a few of his works which differ.
self portrait, 1896, for my friend Daniel

Night Café at Arles

Nirvana Aka Portrait Of Meijer de Haan
In 1888, Dutch painter Meijer de Haan met Pissarro, Theo van Gogh, and Paul Gauguin on the coast of Brittany. Theo introduced him to Vincent and they exchanged letters.
[image error]
The Yellow Christ, 1889, Albright-Knox Art Gallery, Buffalo, NY
Under the influence of folk art and Japanese prints, Gauguin evolved towards Cloisonnism, a style given its name by the critic Édouard Dujardin in response to Émile Bernard's method of painting with flat areas of color and bold outlines, which reminded Dujardin of the Medieval cloisonné enamelling technique. The Yellow Christ is often cited as a quintessential Cloisonnist work.

The Siesta
 Paul Gauguin Thematic Essay
Paul Gauguin Thematic Essay"Gauguin cultivated and inhabited a dual image of himself as, on the one hand, a wolfish wild man and on the other, a sensitive martyr for art."
http://www.metmuseum.org/toah/hd/gaug...
 Heather wrote: "The Nirvana Aka Portrait Of Meijer de Haan reminds me a little of Munch."
Heather wrote: "The Nirvana Aka Portrait Of Meijer de Haan reminds me a little of Munch."It's at the Wadsworth -- it is a tiny painting on board I believe. His face in person is very disturbing. The women are interesting too.




Born to parents who were bohemian musicians, de Vlaminck planned to make a career as a professional cyclist. Like his parents, he also had musical talent and earned a living through the violin. de Vlaminck also had a passionate interest in painting which was fostered by Robichon, a French artist. In 1896 he contracted typhoid fever which ended his racing career. Obliged to support himself and his family, he gave violin lessons and eventually joined the military. It was during one of his military leaves at Chatou, that he met Andre Derain. In June 1900, de Vlaminck and Derain began the school of Chatou which later came to be recognized as the place of origin for the Fauve art movement.
In the ensuing years, he met and was influenced by Henri Matisse, who inspired him to collect African masks, and Pablo Picasso. As a member of the Fauvist movement, which flourished from 1905 to 1908, he exhibited with them at the Salon des Independants and d'Automne. He also published a few novels and books of poetry for which Derain made illustrations. de Vlaminck not only painted but created a great number of woodcut prints. Many of these image reveal the strong influence of Gauguin and Van Gogh who were then his contemporaries.
In painting, de Vlaminck adopted Van Gogh's brightly colored palette, along with the technique of painting with open brushstrokes. This eventually led to his application of paint directly onto the canvas from the tube. de Vlaminck's early body of work epitomizes the Fauve revolution. Around 1908, he grew dissatisfied with what he saw as the formlessness of his early style. He turned his attention to the work of Cézanne and adopted a darker palette, painting many landscapes rendered in a personal expressionist style.
In 1920, he turned to a more naturalistic and formally vigorous style. His late work is dominated by colorful and brooding still lifes and landscapes. Despite his departure from the Fauvist style, Vlaminck continued to travel with Derain during the later years of his life and published dozens of autobiographical accounts of his life and his experiences with other artists. Maurice de Vlaminck died in 1958.